The app for independent voices
Why is Every Newborn Forced to Get the Dangerous Hepatitis B Vaccine? The suppressed history behind the Hep B vaccine and the actual risks and benefits of it we are never told about. By A Midwestern Doctor (09/17/25)
A Midwestern Doctor’s article was written anticipating a decision by CDC’s Advisory Committee for Immunization Practices (ACIP) to remove recommendations to give Hepatitis B vaccines to all newborns.
Unfortunately, ACIP punted during its September 18-19, 2025 meeting, voting to table the decision regarding newborn Hepatitis B vaccines to sometime in the future. Here's a short summary of ACIP September 18-19, 2025 decisions: tinyurl.com/mw8fcxek
So now, more than ever before, it’s important to understand the forgotten history, risks, and benefits of these shots, especially for newborns.
ED NOTE
Parents should read this article carefully, then consider opting out of Hep B vaccines for their newborns, even if you have to give birth at home (with an experienced midwife) or in a birthing center that will respect your wishes.Contents
Hepatitis B Safety Concerns
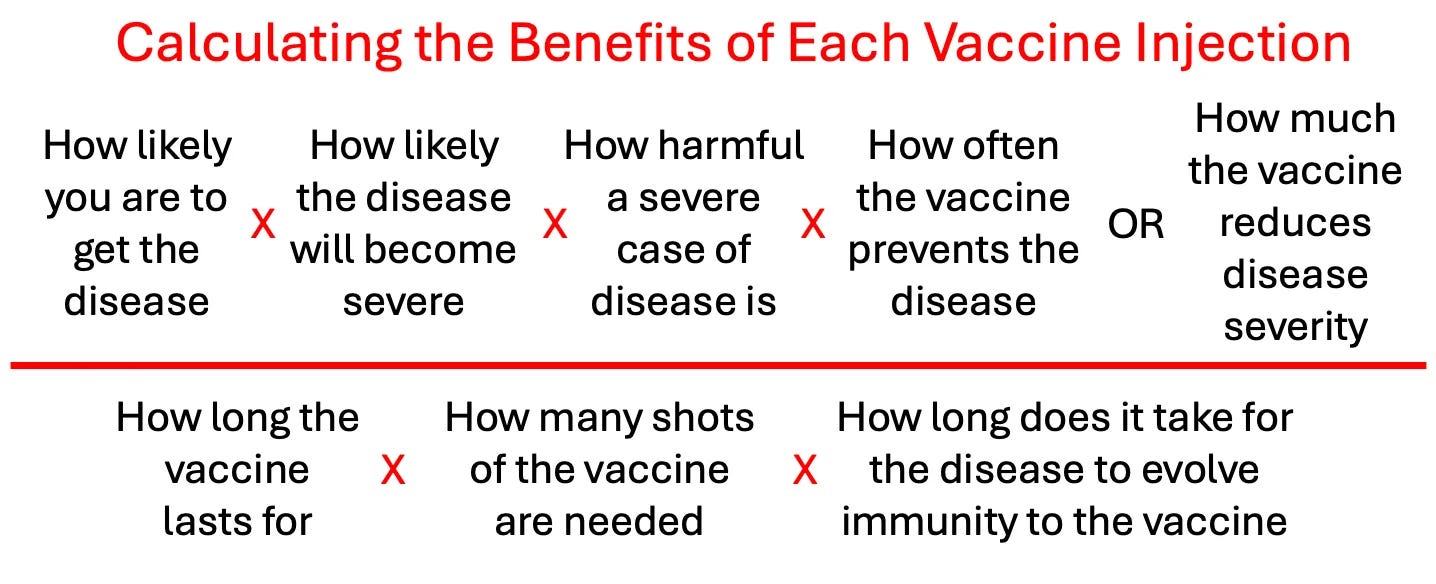
Determining The Risks and Benefits of Vaccines
Hepatitis B Distribution
Hepatitis B Vaccine Efficacy
Hepatitis B Vaccine Design
The History of the Hepatitis B Vaccine
Why is the Vaccine Given?
Conclusion
From the Conclusion
In my view, the saga of the hepatitis B vaccine exemplifies how the government often takes a top-down approach to addressing a challenging issue, even when this approach is not suitable for the circumstances. In turn, the pressure the CDC was under to do something about hepatitis B (given that each successive attempt had failed) made them conclude they had no option but to universally mandate the vaccine, and then to overcome public resistance to this, insist the vaccine was miraculous and completely safe.
As is typical of A Midwestern Doctor’s (AMD) articles, this one is long and filled with careful research and analysis, along with links, data, charts, and videos.
For those without time to read the entire post, we’ve sought help from our friend Grok ai to bring you the essential bits. We do encourage you to look at the images and watch the video clips (most under 6 minutes, some longer), which are quite revealing.
Summary (Grok ai, edited; images from article)
AND discusses the universal hepatitis B vaccine policy for newborns, arguing it offers minimal benefits while posing significant risks including autoimmune disorders. The forgotten history of controversy about this vaccine includes safety concerns and policy shifts from targeting high-risk groups to mass infant vaccination due to failures in adult outreach.
Hepatitis B Vaccine Controversy The hepatitis B vaccine, given to all U.S. newborns since 1991, has faced ongoing debate over its risks and benefits, with much historical context suppressed.
Introduced in 1981 for high-risk groups including gay men, IV drug users, and healthcare workers.
Expanded to newborns despite low transmission risk in this group.
ACIP was supposed to re-evaluate the policy on September 18, 2025, but tabled the discussion to some future meeting.
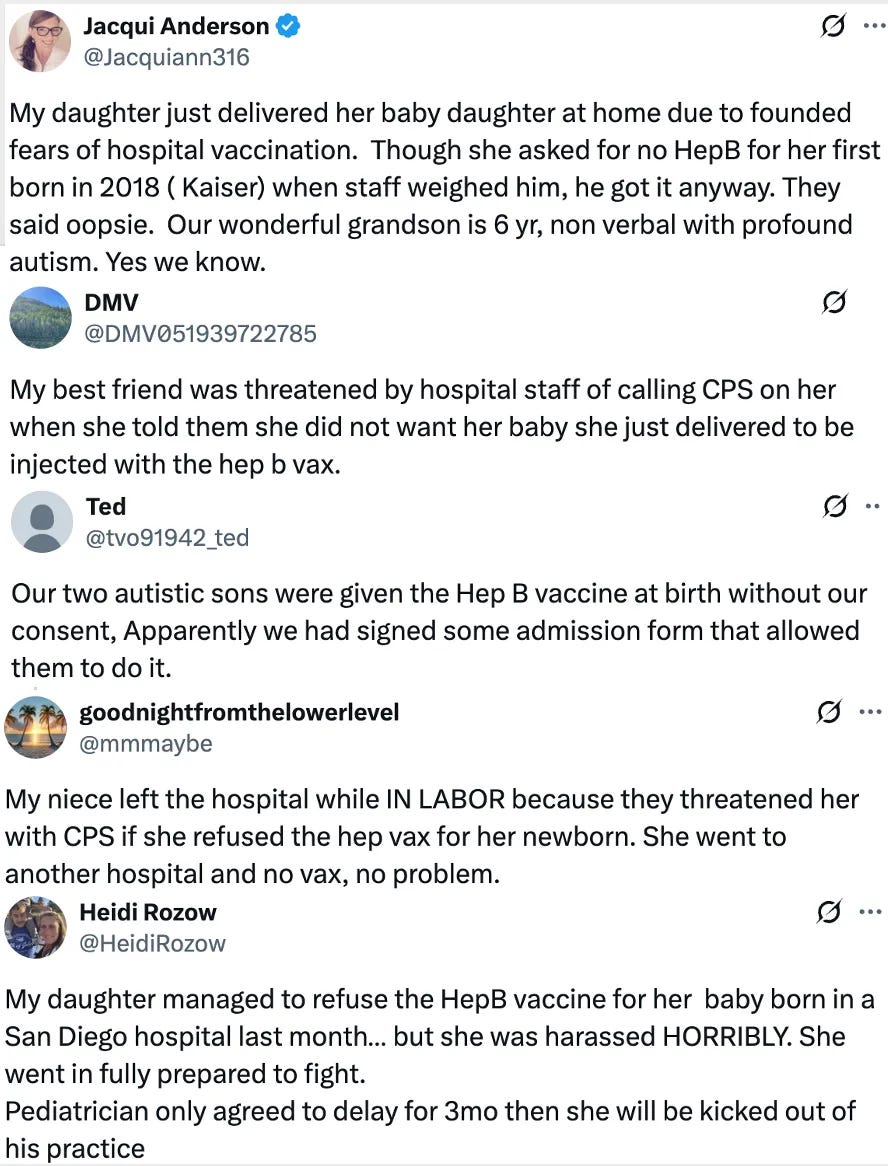
Safety Concerns Numerous studies, often dismissed by authorities, link Hep B vaccine to autoimmune and neurological issues.
Associated with multiple sclerosis, arthritis, lupus, Guillain-Barré syndrome, and more.
VAERS reports show injuries far outnumber prevented cases in infants.
Early trials monitored side effects for only 4-5 days; long-term studies lacking.
2005 study showed 60% of recipients developed myelin reactivity.
Risks and Benefits Analysis Vaccine reduces acute cases in high-risk adults but shows no impact on chronic hepatitis B prevalence.
Low U.S. prevalence (under 2%).
Main transmission is via sex, needles, or birth.
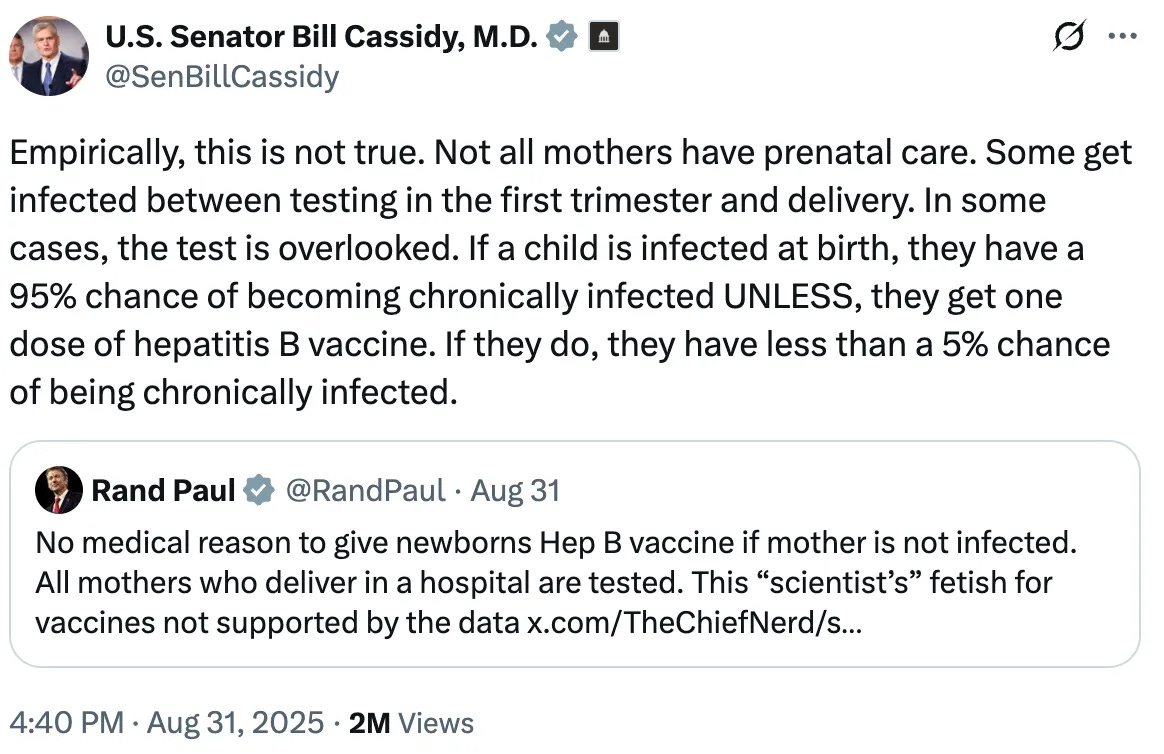
Newborn vaccination prevents ~1 maternal transmission per million doses.
Antibodies wane before adolescence; 1.5-3.5% have breakthrough infections post-vaccination.
No decline in chronic cases despite decades of infant vaccination.
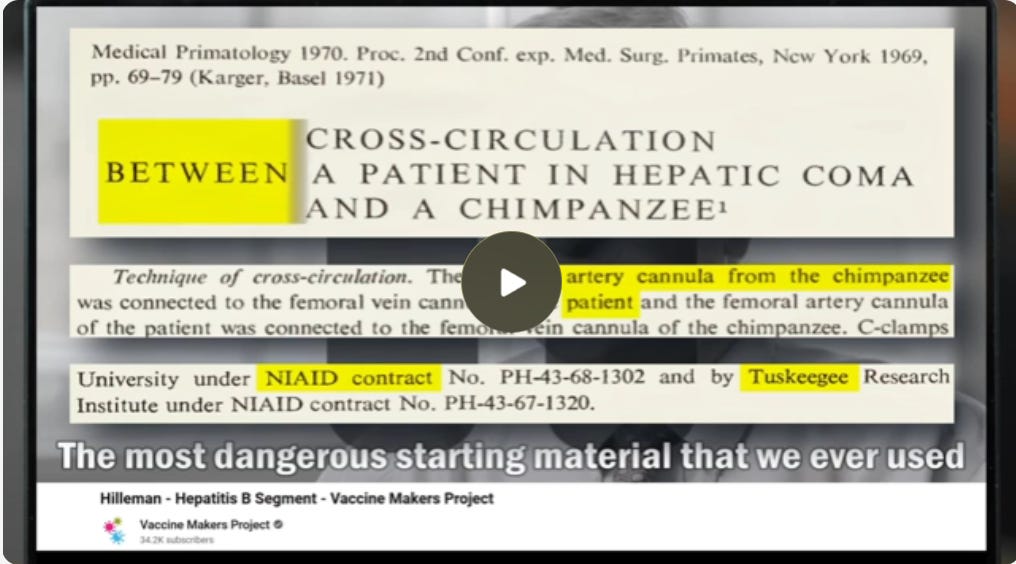
Historical Development Vaccine originated from plasma of infected individuals, with early trials in gay communities.
Possible HIV contamination in 1970s-1980s trials, matches AIDS emergence.
Shift to recombinant version in 1986, likely due to the contamination.
Policy to mass vaccinate newborns likely due to high manufacturing costs, low adult uptake, and failure to target at-risk groups.
Reasons for Newborn Mandate Official rationale (preventing undetected maternal transmission) is weak; actual motive was to vaccinate before high-risk behaviors begin.
A past ACIP member revealed aim to capture "inner city youth" via hospital births.
Newborn mandate overcomes adult non-compliance and ensures early immunization compliance.
Ignores safer alternatives or exemptions for hepatitis-negative mothers.
Conclusion and Call to Action Policy exemplifies flawed top-down approach; AMD urges public support for ACIP re-evaluation to end universal newborn vaccination.
Related:
COVID Essential Links (search for Hepatitis B): tinyurl.com/4x23jysr
FDA Package Insert Hepatitis B Vaccine: