The app for independent voices
I’ve always been fascinated by the balance between 𝑺𝒊𝒎𝒑𝒍𝒊𝒄𝒊𝒕𝒚 𝒂𝒏𝒅 𝑷𝒐𝒘𝒆𝒓 𝒊𝒏 𝑻𝒆𝒄𝒉𝒏𝒐𝒍𝒐𝒈𝒚. Some tools, like JSON Web Tokens, manage to do so much with so little: compact, elegant and quietly essential 🖤
𓎆
Let’s unravel what makes JWTs so indispensable.
𓎆
→ What is JWT?
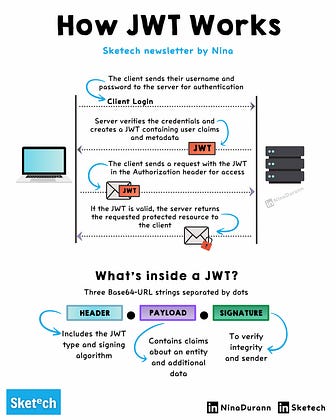
JWT is an open standard (RFC 7519) for securely transmitting information between parties as a JSON object.
Structure: Composed of three parts separated by dots (.) - Header, Payload, and Signature.
𓎆
→ Components of JWT
Header: Contains metadata about the token, typically the type of token and the signing algorithm.json
{ "alg": "HS256", "typ": "JWT" }
Payload (Claims): Contains the actual data. This includes registered claims (like iss, exp, sub), public claims, or private claims.json
{ "sub": "1234567890", "name": "John Doe", "iat": 1516239022 }
Signature: Ensures the token hasn't been tampered with. It's created by encoding the header and payload, then signing with a secret or private key.
𓎆
→ How JWT Works
Token Creation: The server generates a JWT when the user logs in.
Token Transmission: This token is sent to the client (e.g., browser).
Token Usage: For subsequent requests, the client sends the JWT, which the server verifies before granting access.
𓎆
→ Advantages
Stateless: Servers don't need to store session information.
Scalability: Ideal for distributed systems and microservices.
Flexibility: Can be used across different domains.
𓎆
→ Security Considerations
Encryption vs Signing: JWTs are signed, not encrypted by default. Use JWE (JSON Web Encryption) for end-to-end encryption.
Token Expiry: Always set an expiration time to limit token lifetime.
Secure Transmission: Use HTTPS to prevent token interception.
𓎆
→ Implementing JWT
Backend: Use libraries like jsonwebtoken in Node.js or PyJWT in Python.
Frontend: Store tokens in HTTP-only cookies or local storage with caution.
𓎆
Hey! I'm Nina, a software tech lead sharing fresh visuals engineers love through my newsletter Sketech. Follow to Decode Complexity ❤️ sketechnews.substack.com